Now Reading: HIIT Workouts for Rapid Fat Loss
-
01
HIIT Workouts for Rapid Fat Loss
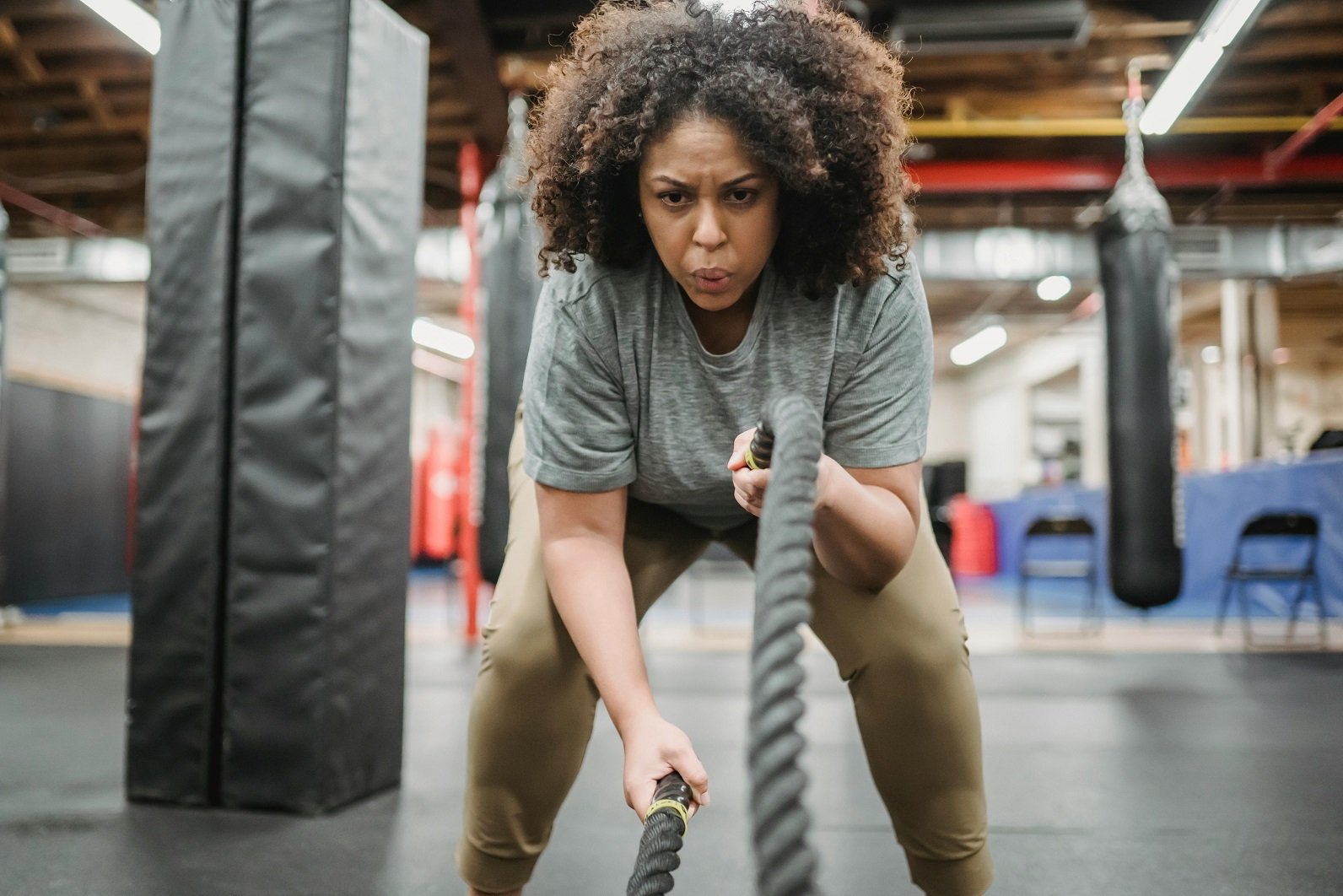

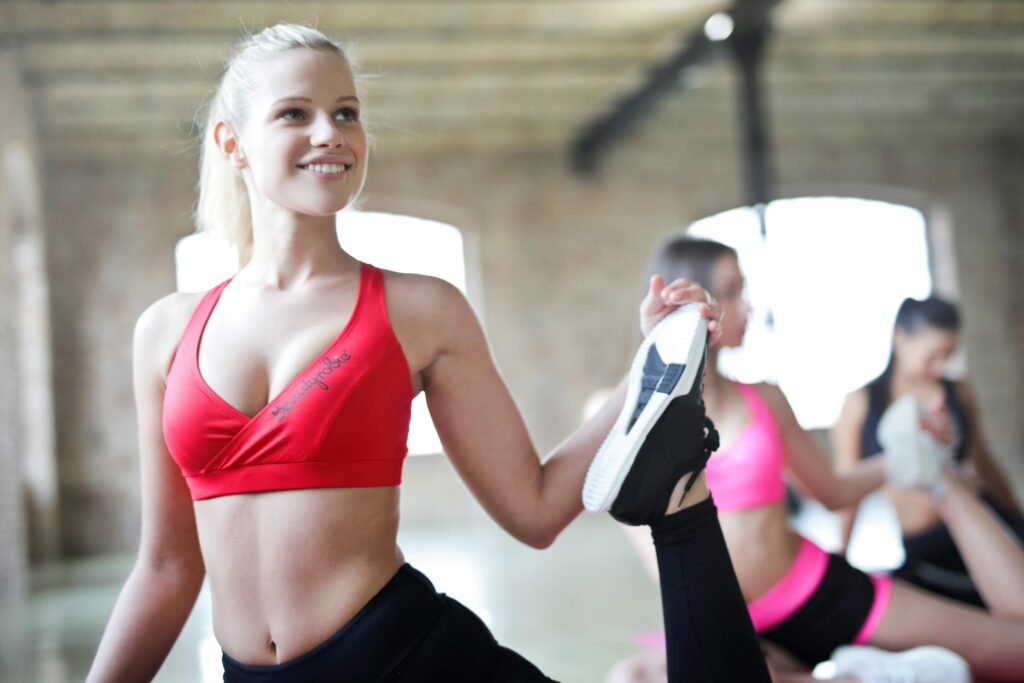
Among various workout methods, none are as efficient and time-saving as HIIT workouts when it comes to fitness and weight control. High-Intensity Interval Training, or HIIT, has become extraordinarily popular due to its effectiveness in quickly eliminating fat and at the same time increasing the person’s overall fitness level. As the name of the website weightlossformula.com suggests, we concentrate on verified methods that give real results, and HIIT workouts are considered by many to be one of the most powerful tools for quick fat loss.
HIIT workouts aim at bringing your body to the max during very short repetitions of hard exercise that are separated by only a brief rest period. The calorie burning is tremendously high during such a short time span and the good thing is that fat continues to be burned long after the workout. This extensive guide will explain to you the principles and mechanisms of HIIT, its outstanding features as a fat loss technique, and how to adapt it to your fitness regimen safely and in a way that it lasts.
What HIIT Is and Its Mechanism?
High-Intensity Interval Training, or HIIT, is a type of workout that consists of maximum effort intervals followed by a short recovery. Compared to the standard steady-state exercises such as jogging or cycling at a uniform pace, HIIT will put to work both your aerobic and anaerobic systems. The very quick and efficient adaptation of the body as a result of the dual stimulation is what leads to the development of endurance, strength, and fat burning.
In the high-intensity intervals, the heart rate escalates very quickly, thereby making the body heavily dependent on the energy that is stored. Yet, during the recovery phase, the heart rate goes down a bit, but the metabolism stays high. This process goes on repeatedly during the entire workout session, thereby causing a very powerful metabolic response that makes fat loss quick.
Why HIIT Workouts Are So Effective for Fat Loss
Metabolism effect is one of the major reasons HIIT workouts are perfect fat loss. HIIT triggers the phenomenon known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption, which is usually called the “afterburn effect”. The effect implies that the metabolism continues burning calories for hours and, in some cases, even up to 24 hours after the workout is finished.
HIIT workouts take it a step further by helping one maintain their muscularity while losing fat. Long cardio sessions can sometimes result in the loss of muscle, especially when performed along with a caloric deficit diet. HIIT, on the contrary, activates the muscle fibers and makes your body use fat while retaining muscle.
The efficiency of HIIT is another major advantage. Many HIIT routines can be done in as little as 20 to 30 minutes, which makes them ideal for those who have tight schedules. Yet, despite the shorter time, these workouts usually result in the same or even greater fat loss compared to longer, low-intensity sessions.
HIIT vs Cardio v. Weight Loss
With long-lasting effects and consisting of activities like walking, jogging, or cycling, cardio exercises are very effective for the improvement of heart and blood vessels health and the fat loss however; the latter still requires a long time before the real fat loss happens. HIIT, meanwhile, was found to be a quicker method for fat burning and sometimes more efficient than the former.
The steady-state aerobics mainly extract the calories during the exercise itself, while HIIT session is approximately one and half times longer than the activity time in terms of calorie burning because of the metabolism boost that happens after the exercise. In addition, the HIIT routine supports the improvement of insulin sensitivity, which is practically making it easier for the organism to utilize carbohydrates for energy rather than storing them as fats.

How HIIT Helps in Quick Fat Loss
HIIT workouts are effective for fat loss due to a number of physiological changes in the body. Firstly, they push the body to burn more calories over a very short period of time. Secondly, they support hormonal responses with increased production of growth hormone and adrenaline, both of which are associated with the mobilization of fat.
HIIT also works on the mitochondria which are the powerhouses of cells. Thus, your body will be able to produce energy in a more efficient way. The body will naturally start to use fat for energy even when you are not exercising. The daily practice of HIIT will result in gradual reduction of body fat percentage.
HIIT Workouts – Fat Loss Types
HIIT workouts could be done with a variety of exercises and thus are the best workout for everyone regardless of their fitness levels. Bodyweight HIIT workouts are the most favorite since they don’t need any equipment and are able to be done anywhere. Squats, lunges, push-ups, mountain climbers, and burpees are among the exercises that are used to establish the frequency of intense intervals.
HIIT workouts based on cardio comprise activities such as sprinting, cycling, rowing, or rope jumping. They are perfect for burning a lot of calories and boosting one’s cardiovascular endurance.
Strength-based HIIT workouts mix resistance training with high-intensity intervals. This method not only helps in fat loss but also in muscle gain, which results in a toned and athletic look. Incorporating weights into HIIT can double the fat burning effect over time.
How Often Should HIIT Be Done for Losing Fat?
Although HIIT training is very efficient, it takes much out from the body as well. If HIIT is done too often without proper rest, it can cause exhaustion, injury, or even burnout. Rapid fat loss can be achieved by doing two to four HIIT sessions a week for most individuals.
Besides, rest days or low-intensity activities such as walking, stretching, or yoga are very important for recovery. Good recovery gives time for your muscles to heal and grow while avoiding overtraining.

HIIT Workouts and Nutrition for Maximum Results
Nutrition is a major thing that determines how effective HIIT workouts can be in terms of burning fat. A balanced diet with enough protein, good fats, and complex carbs is essential as it not only helps in muscle recovery but also supports energy levels.
A small meal consisting of protein and carbs taken before a HIIT workout can lead to better performance, whereas a post-workout meal rich in protein aids in muscle tissue repair and retaining lean mass. Hydration is also a very important factor as the sweating during HIIT leads to a considerable loss of fluids.
HIIT for Beginners: Getting Started Safely
HIIT workouts are not only for professionals. One can make them suitable for beginners by decreasing both intensity and duration. Newcomers can develop their strength and stamina without putting themselves at risk of injury by doing shorter work intervals that are followed by longer rest periods. A proper warm-up is also a must for any HIIT workout routine, as well as a proper cool down afterward.
The most important factor when performing HIIT is to listen to one’s own body. It is normal to feel tired but do not ignore pain or dizziness. Increasing the intensity gradually over time will result in consistent progress along with fat loss that can be maintained.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with HIIT Training
One common mistake is doing HIIT workouts at a moderate intensity instead of true high intensity. If HIIT is done properly, the work intervals should feel like a challenge and almost getting to your maximum effort.
Another error is overlooking recovery. HIIT can cause a lot of stress on the nervous system and muscles, thus it is very important to have rest days for success in the long run. Wrong posture while doing exercises is also a common problem and can cause injury. Concentrating on right technique makes the workouts not only safe but also more productive.
Long-Term Advantages of HIIT Workouts
Besides quick fat loss, HIIT workouts also provide many long-lasting health benefits. They enhance cardiovascular health, boost muscle tone, improve endurance, and assist in better blood sugar control. HIIT is also associated with better mental focus and lower stress levels.
The adaptability and versatility of HIIT workouts allow for modifications as your fitness level increases, thus making them a sustainable option for long-term weight management.
Conclusion
There is a consensus at weightlossformula.com that truly efficient fat loss must be efficient, sustainable, and scientifically valid. HIIT workouts are all three, thus, making them one of the quickest ways of fat loss through the best exercise methods.
No matter if you want to shed pounds, get fitter, or just be healthier in general, including HIIT workouts into your schedule can bring about significant results in a shorter time frame. When along with suitable food, enough sleep, and regularity, HIIT can transform you and allow you to keep losing weight for a long time.
In case you need a reliable method to speed up your fat loss process, HIIT workouts could be the missing element in your weight loss formula that will help you regain control of your fitness journey.
Related Posts
Previous Post
Next Post
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Workout3 days ago
HIIT Workouts for Rapid Fat Loss